When there are new changes in the remote, you need to pull those changes down to your local repo.
There are two steps to bringing over changes from a remote repository into a local repository: fetch and merge.
- Fetch is the act of downloading the latest changes from the remote repository, but without applying them to your current branch yet. It updates metadata in your repo so that it knows what has changed in the remote repo, but your own local branch remains untouched.
- Merge is what you do after fetching, to actually incorporate the fetched changes into your local branch. It combines your local branch with the changes from the corresponding branch from the remote repo.
Scenario You have cloned a remote repo. After you have cloned, two new commits have been added to it. R and L1 in the diagram below represents this scenario.
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "add assets.txt"
commit id: "add goals.txt"
commit id: "[HEAD → main] add loan to Chang"
origin]
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "[HEAD → main][origin/main] add assets.txt"
2 commits behind the remote]
→
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "add assets.txt"
commit id: "add goals.txt"
commit id: "[HEAD → main][origin/main] add loan to Chang"
the missing commits]
Target Now, you wish to bring over those missing commits to your clone, taking it from the state L1 to state L2 (as given in the diagram above).
Preparation
1 Verify the local repo is unaware of the extra commits in the remote.
git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
nothing to commit, working tree clean
The revision graph should look like the below:

If it looks like the below, it is possible that Sourcetree is auto-fetching data from the repo periodically.
2 Fetch from the new remote.
Use the git fetch <remote> command to fetch changes from a remote. If the <remote> is not specified, the default remote origin will be used.
git fetch origin
remote: Enumerating objects: 8, done.
... # more output ...
afbe966..b201f03 main -> origin/main
Click on the Fetch button on the top menu:

3 Verify the fetch worked i.e., the local repo is now aware of the two missing commits. Also observe how the local branch ref of the main branch, the staging area, and the working directory remain unchanged after the fetch.
Use the git status command to confirm the repo now knows that it is behind the remote repo.
git status
On branch main
Your branch is behind 'origin/main' by 2 commits, and can be fast-forwarded.
(use "git pull" to update your local branch)
nothing to commit, working tree clean
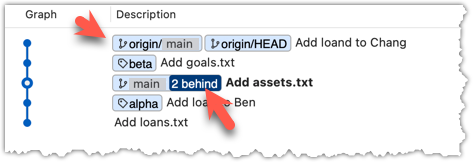
Now, the revision graph should look something like the below. Note how the origin/main ref is now two commits ahead of the main ref.

4 Merge the fetched changes.
Use the git merge <remote-tracking-branch> command to merge the fetched changes. Check the status and the revision graph to verify that the branch tip has now moved by two more commits.
git merge origin/main
Updating afbe966..b201f03
Fast-forward
goals.txt | 1 +
loans.txt | 1 +
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 goals.txt
Verify the status of the repo is as expected:
git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
git log --oneline --decorate
b201f03 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD) Add loan to Chang
1b923a4 Add goals.txt
afbe966 Add assets.txt
0434002 Add loan to Ben
fd96227 Add loans.txt
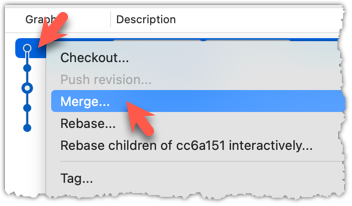
To merge the fetched changes, right-click on the latest commit on origin/remote branch and choose Merge.
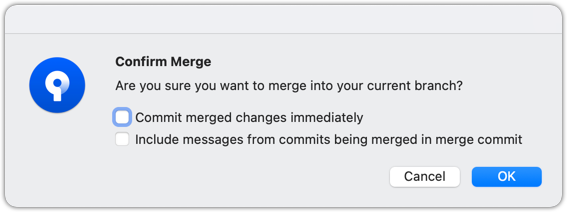
In the next dialog, choose as follows:
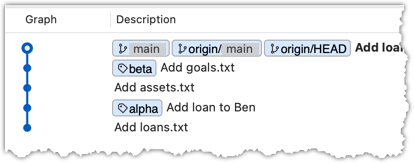
The final result should be something like the below (same as the repo state before we started this hands-on practical):
Note that merging the fetched changes can get complicated if there are multiple branches or the commits in the local repo conflict with commits in the remote repo. We will address them when we learn more about Git branches, in a later lesson.
done!
Pull is a shortcut that combines fetch and merge — it fetches the latest changes from the remote and immediately merges them into your current branch. In practice, Git users typically use the pull instead of the fetch-then-merge.
pull = fetch + merge
Scenario Same as previous hands-on practical.
Target Same as the previous, but this time we intend to fetch and merge in one step.
Preparation
1 Pull the newer commits from the remote, instead of a fetch-then-merge.
Use the git pull <remote> <branch> command to pull changes.
git pull origin main
remote: Enumerating objects: 8, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (8/8), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 6 (delta 1), reused 6 (delta 1), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (6/6), 557 bytes | 69.00 KiB/s, done.
From https://github.com/git-mastery/samplerepo-finances-2
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
afbe966..b201f03 main -> origin/main
Updating afbe966..b201f03
Fast-forward
goals.txt | 1 +
loans.txt | 1 +
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 goals.txt
The following works too. If the <remote> and <branch> are not specified, Git will pull to the current branch from the remote branch it is tracking.
git pull
Click on the Pull button on the top menu:

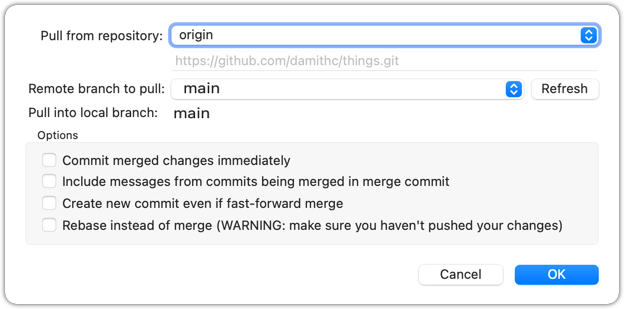
2 Verify the outcome is same as the fetch + merge steps you did in the previous hands-on practical.
done!
You can pull from any number of remote repos, provided the repos involved have a shared history. This can be useful when the upstream repo you forked from has some new commits that you wish to bring over to your copies of the repo (i.e., your fork and your local repo).
Scenario You have forked and cloned a remote repo. Since then, new commits have been added to the original remote repo that you forked from.
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "add assets.txt"
commit id: "add goals.txt"
commit id: "[HEAD → main] add loan to Chang"
upstream: the original remote repo
that you forked]
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "[HEAD → main] add assets.txt"
origin: your fork (remote),
2 commits behind upstream]
gitGraph BT:
%%{init: { 'theme': 'default', 'gitGraph': {'mainBranchName': 'main'}} }%%
commit id: "add loans.txt"
commit id: "add loan to Ben"
commit id: "[HEAD → main][origin/main] add assets.txt"
2 commits behind]
Target Now, you wish to bring over new commits to your clone, and also update your fork with those commits.
Preparation
1 Confirm your local repo is behind by two commits. Here are two alternative ways to do that:
a) Go to the upstream repo at https://github.com/git-mastery/samplerepo-finances-2, and navigate to the page that lists commits of the repo. Compare that list of commits to the list of commits in your local copy.
OR
b) Do a fetch and examine the revision graph locally, as shown below.
git fetch upstream
git log --oneline --decorate --graph --all
* b201f03 (upstream/main, upstream/HEAD) Add loan to Chang
* 1b923a4 Add goals.txt
* afbe966 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD) Add assets.txt
* 0434002 Add loan to Ben
* fd96227 Add loans.txt
2 Pull from the upstream repo. If there are new commits, those will come over to your local repo. For example:
git pull upstream main
3 Push to your fork. Any new commits you pulled from the upstream repo will now appear in your fork as well. For example:
git push origin main
The method given above is the more 'standard' method of synchronising a fork with the upstream repo. In addition, platforms such as GitHub can provide other ways (example: GitHub's Sync fork feature).
done!
SIDEBAR: Distributed vs Centralised Revision Control
Revision control can be done in two ways: the centralized way and the distributed way.
Centralized RCS use a single central (server-hosted) repository that is shared by the team. Developers check out a working copy, make changes locally, and then commit directly to the central repository. Instead of having their own copy of the entire repository history, they only have a working copy of files. One advantage of this model is having a clear and single "source of truth." One big disadvantage is that the central server becomes a critical dependency: if it's down, most operations (commits and history queries beyond the local working copy) are blocked. Older RCS tools such as CVS, Subversion, and Perforce follow this model.
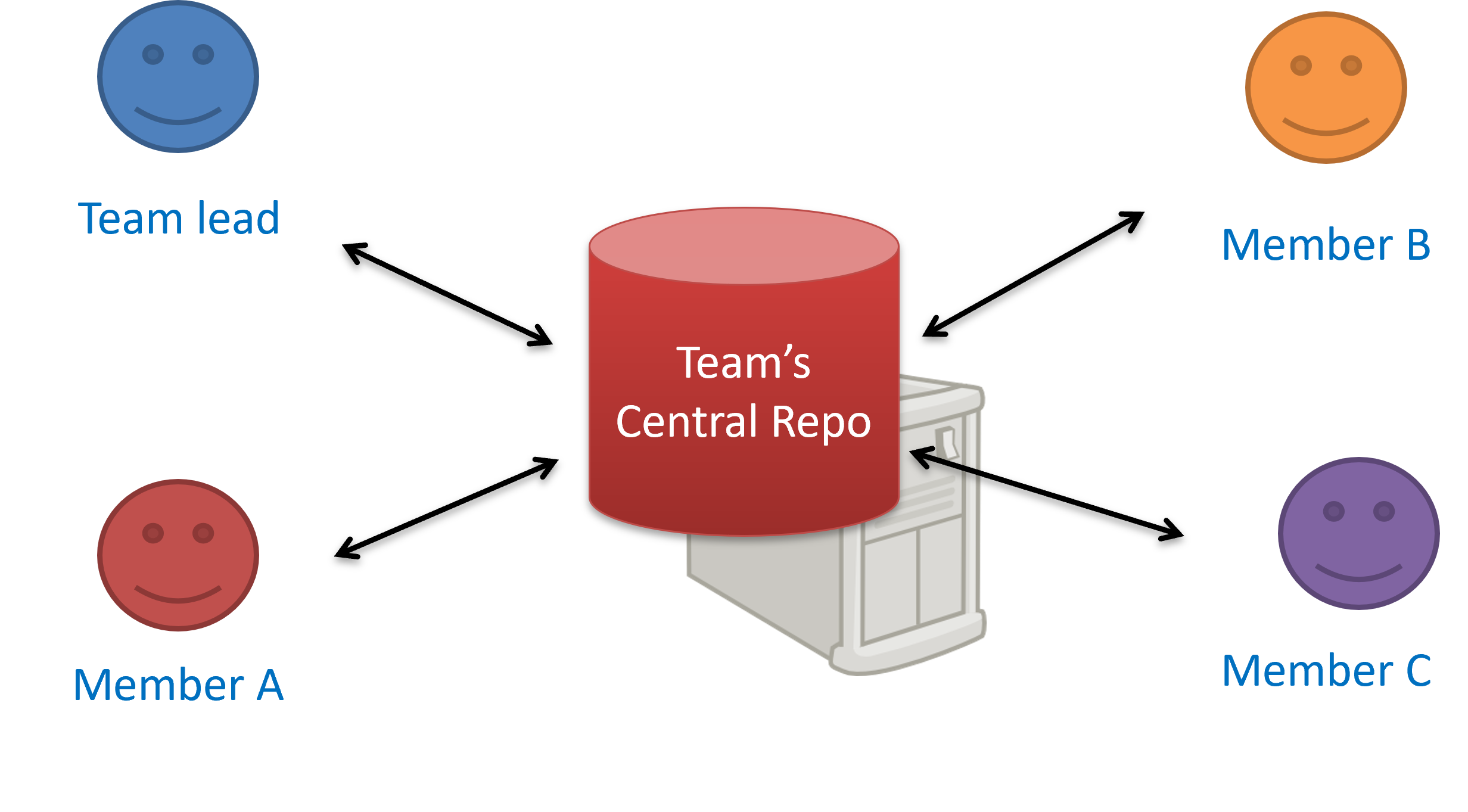
The centralized RCS approach
Distributed RCS (also known as decentralized RCS) allow multiple remote and local repositories to work together. The workflow can vary from team to team. For example, every team member can have their own remote repository in addition to a local repository. This architecture enables offline work, fast local operations, and more flexible workflows. It also supports multiple integration points (e.g., forks or alternative remotes) and uses cryptographic checksums to ensure history integrity. The trade-offs include more conceptual complexity (multiple repositories, remotes, and sync patterns) and the need for conventions to establish an authoritative integration flow. Git and Mercurial are prominent RCS tools that support the distributed approach.
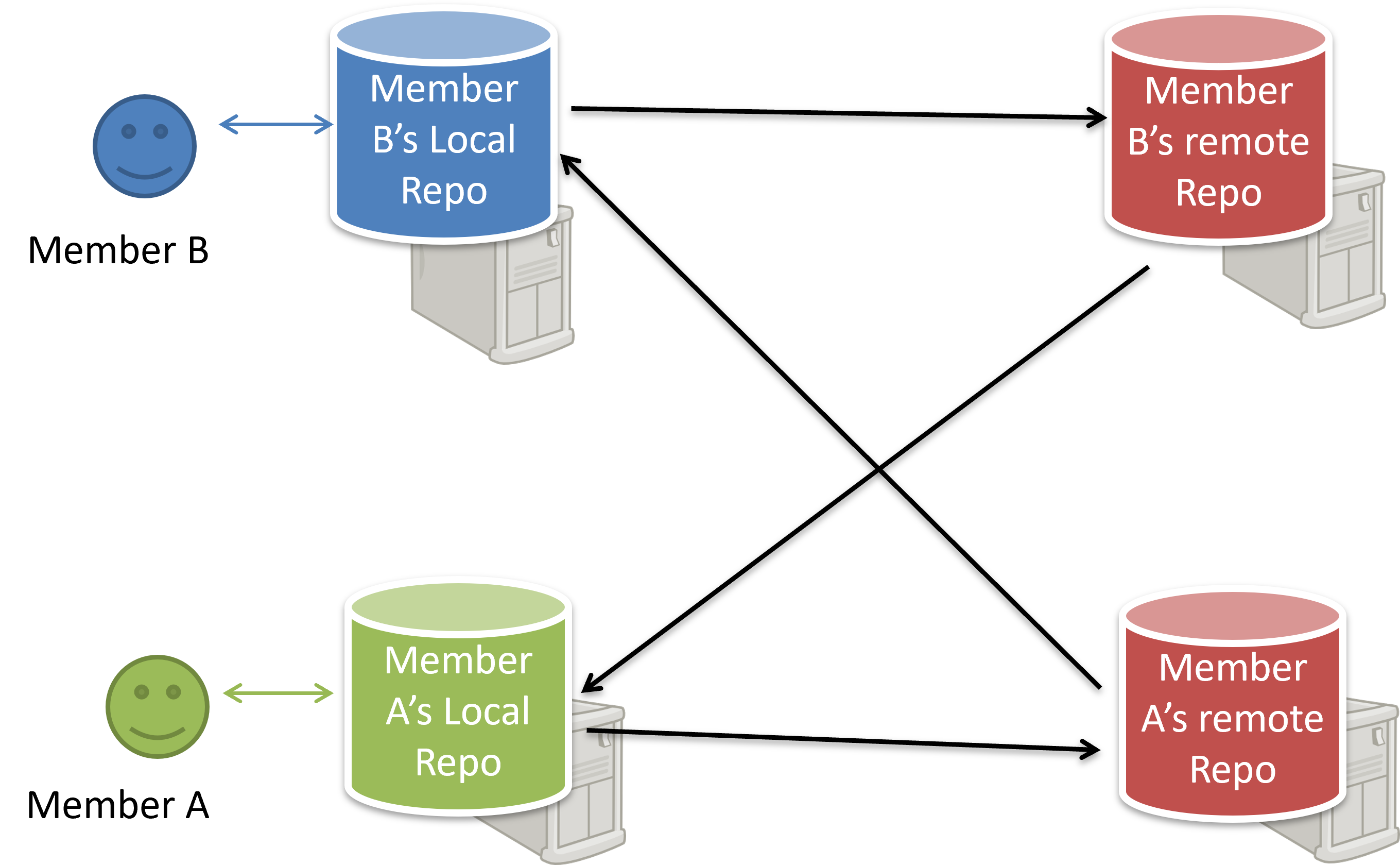
The decentralized RCS approach
Given its use of multiple copies of a repository, Git is considered a distributed revision control software, as opposed to a centralised revision control software that keep only a single repository.